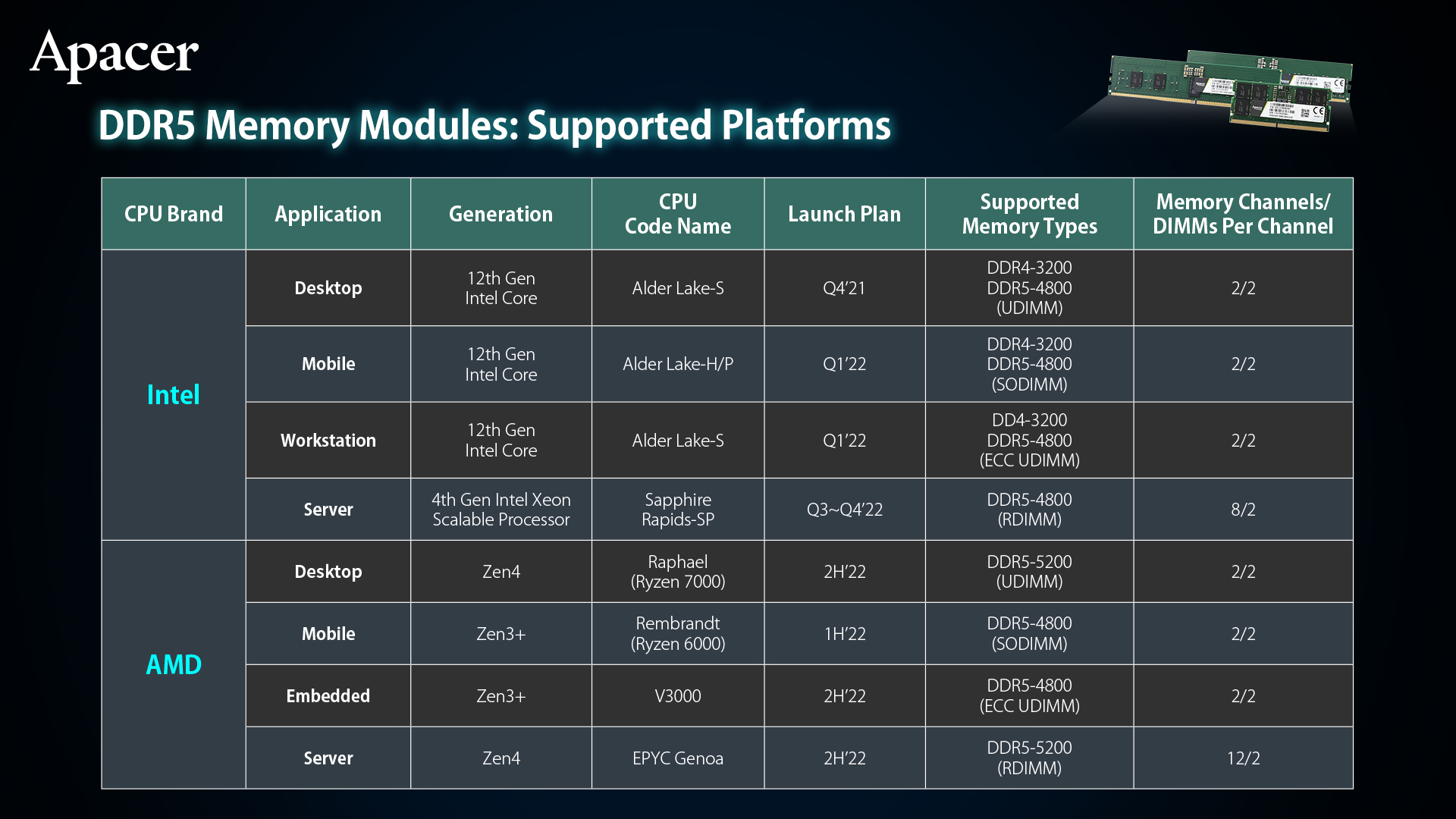
As industrial applications increasingly rely on intelligent data processing, Embedded AI and edge computing workloads are driving demand for memory solutions capable of handling massive data throughput with low latency. With the rapid advancement of processor platforms, industrial systems are entering a new era of high-speed computing and intelligent workloads. Following Intel’s release of the 12th-generation Core desktop processors (Alder Lake), next-generation server platforms such as Intel Eagle Stream and AMD Zen4 Genoa have accelerated the adoption of next-generation memory technologies across industrial markets. These platforms represent a pivotal milestone for DDR5 memory, enabling its deployment across industrial, embedded, and server-class applications and positioning DDR5 as a foundational technology for future-ready system designs.
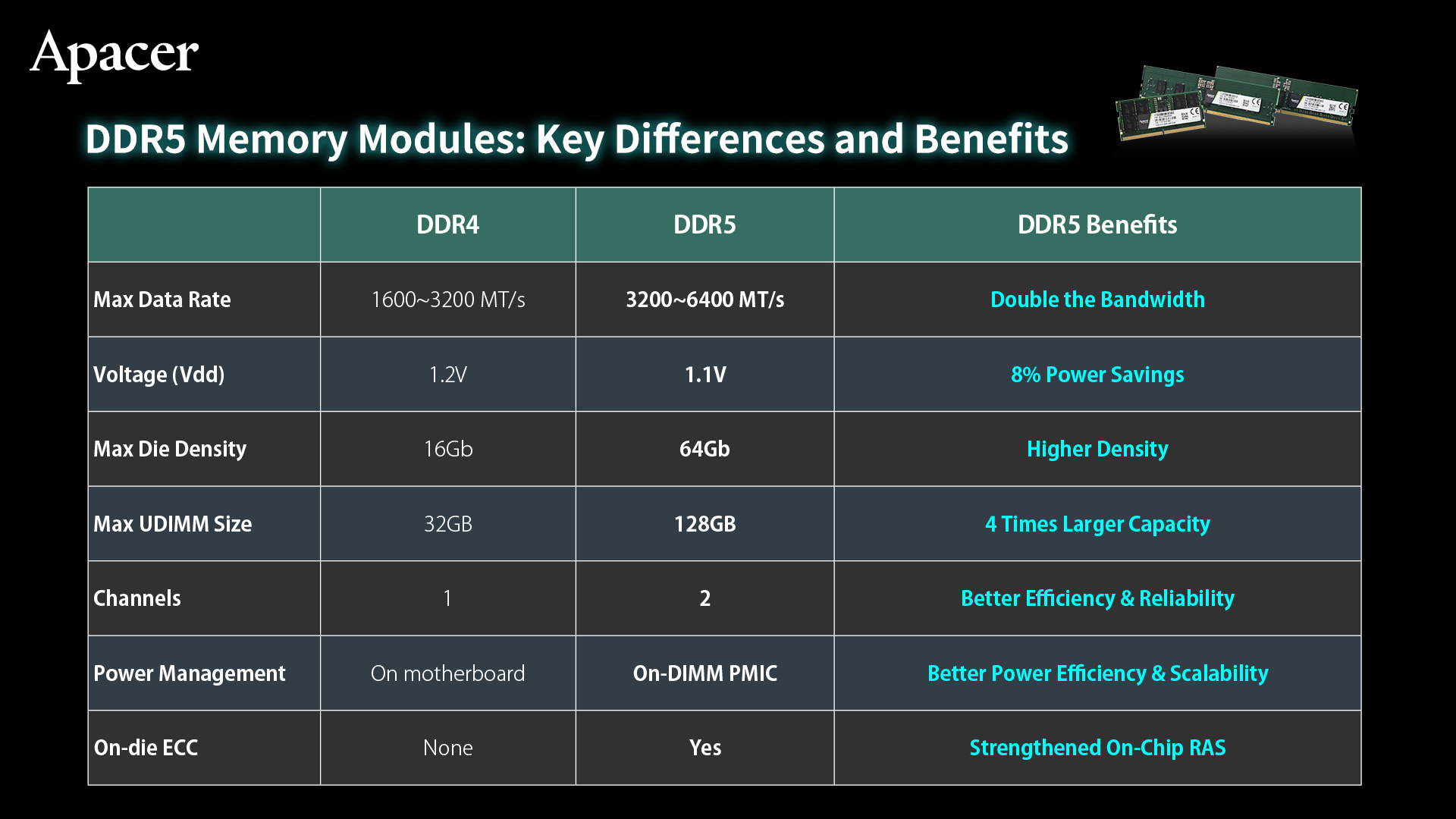
Compared to its predecessor, DDR5 memory delivers a substantial leap in performance, offering double the bandwidth of DDR4 and up to 50% higher data transfer rates at an initial speed of 4800 MHz versus 3200 MHz. Beyond performance gains, DDR5 introduces improvements in capacity scalability, stability, and power efficiency—key enablers for green computing initiatives. These advancements make DDR5 particularly well suited for data-intensive environments such as enterprise servers, data centers, and industrial high-speed computing systems, where reducing power consumption while maintaining sustained performance is essential for long-term operational efficiency.
DDR5 RDIMM industrial server memory is designed to meet these requirements, delivering reliable operation under heavy workloads while enabling faster data transfers and improved system responsiveness for real-time, data-driven decision-making at the edge. However, what are the differences in technical specifications of DDR5 RDIMMs, which demand special attention during product development? When adopting DDR5 industrial memory, what’s the best way to grasp the advantages and seize the market opportunity?
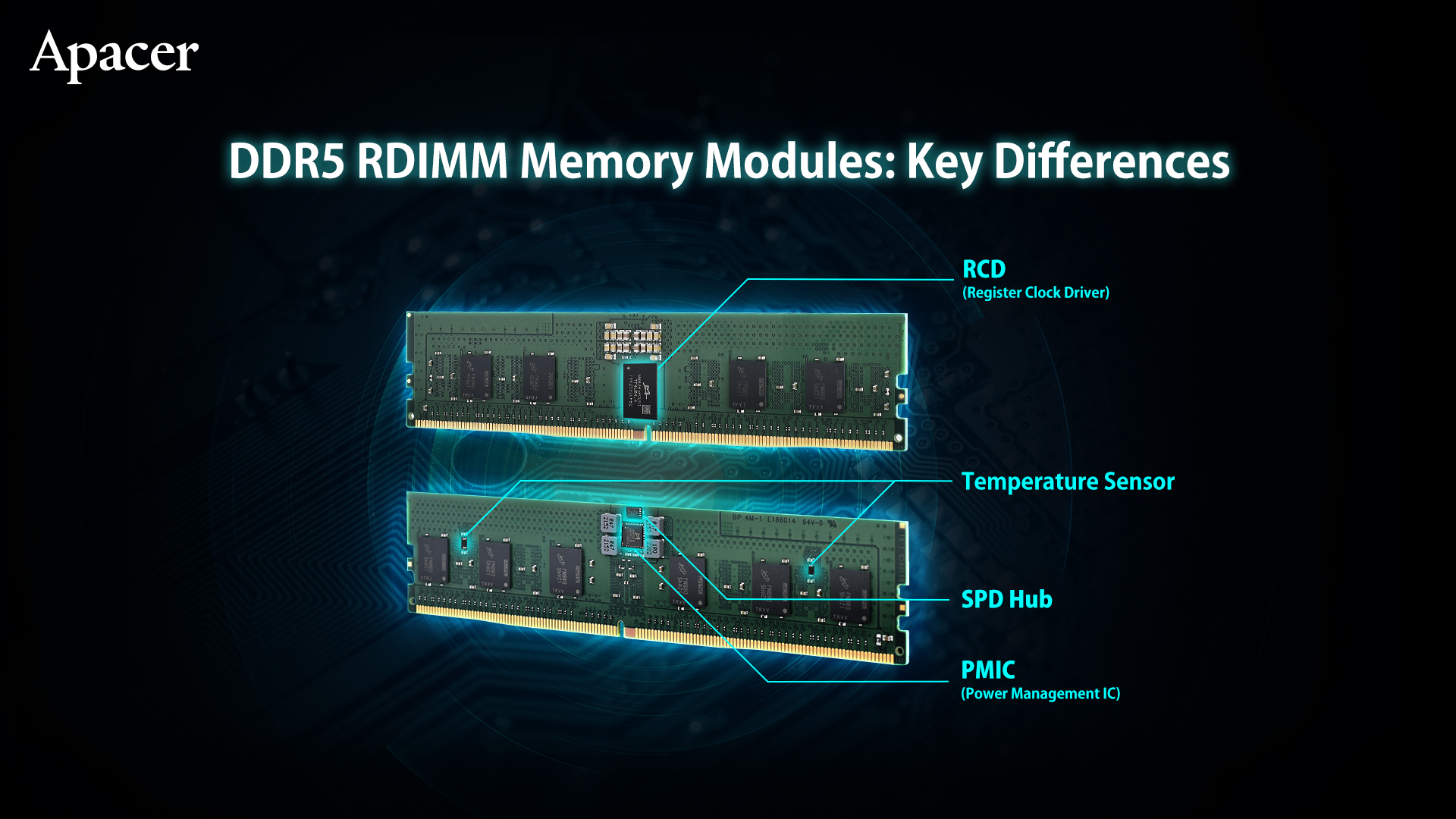
DDR5 RDIMM Server Memory Modules - Key Specification Differences
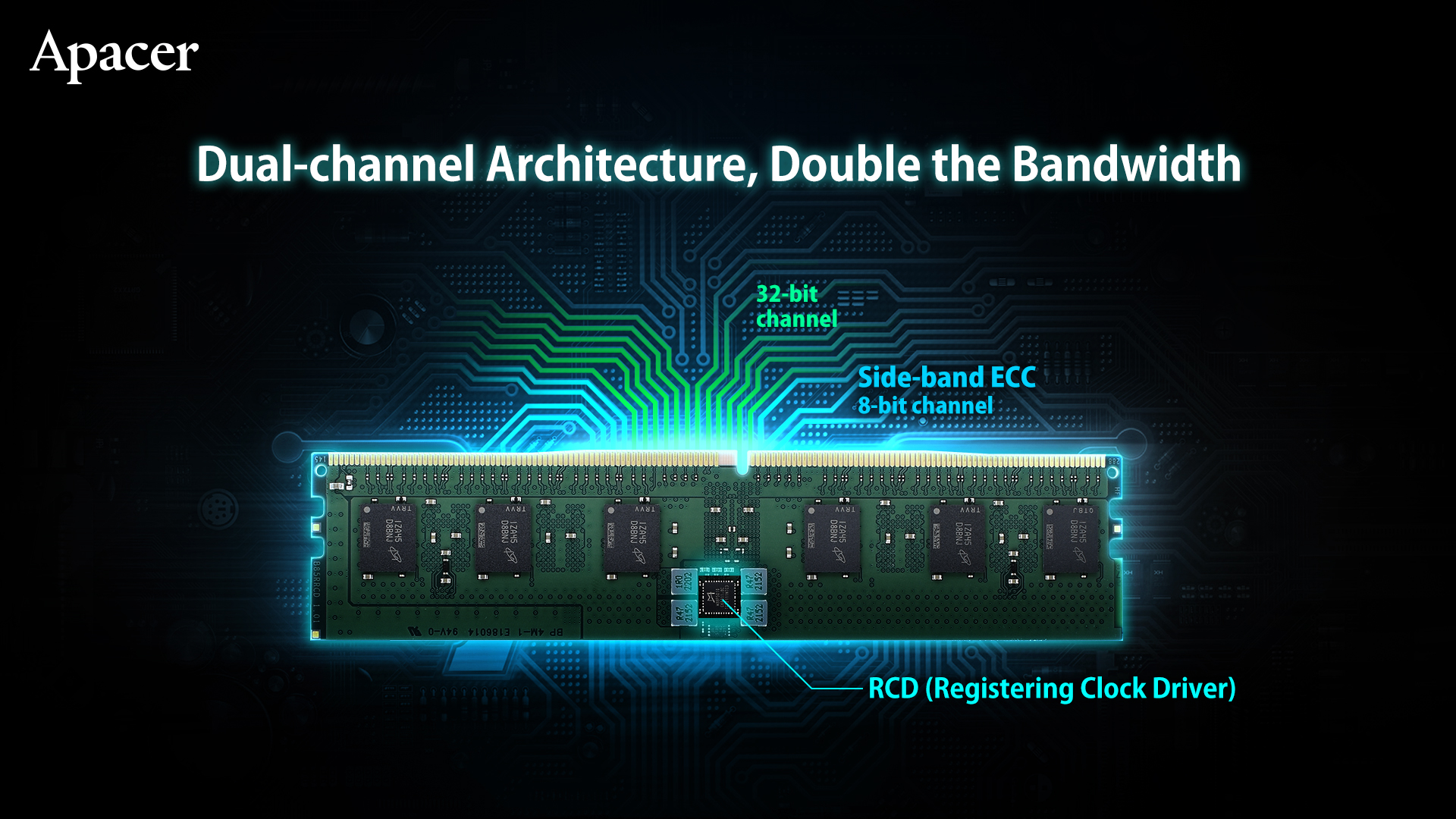
1. Dual-channel Architecture, Double the Bandwidth
DDR5 memory is developed with a new channel architecture, providing two sets of completely independent 32-bit sub-channels. Not only does the double bandwidth mode improve overall performance, but it also effectively shortens access latency and improves channel efficiency.
The DDR5 RDIMM server memory has dual 40-bit sub-channels, adding 8 bits to the existing 32 bits of each channel to support ECC error detection and correction mechanism. The design of the RCD (Registering Clock Driver) can further reduce the load of the CPU, strengthen the signal integrity and reduce interference.
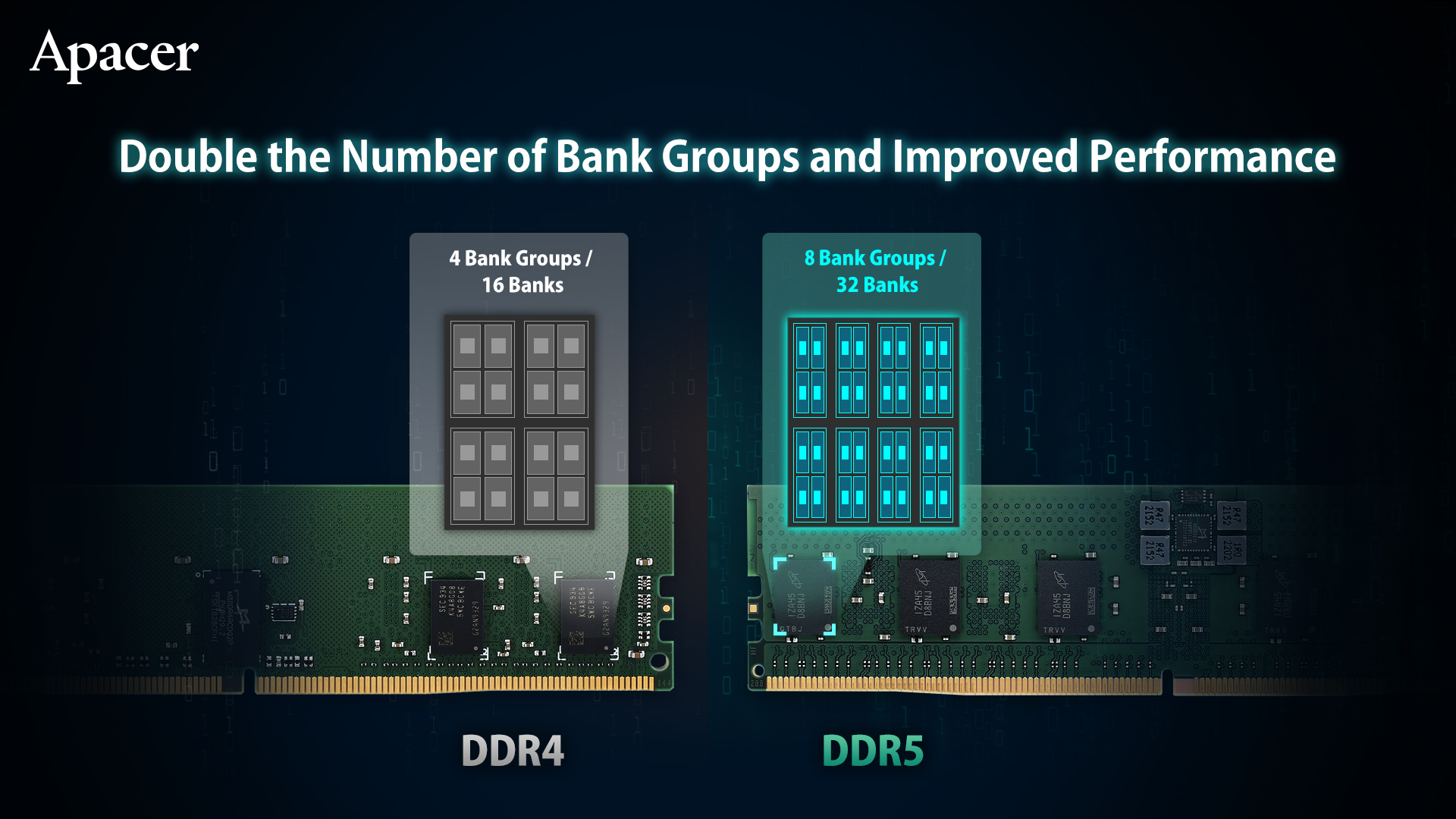
2. Double the Number of Bank Groups and Improved Performance
Compared with DDR4, the bank groups of DDR5 memory have increased from 4 to 8, and the total number of banks has also increased from 16 to 32. The number of bank groups is doubled, which helps to increase the amount of data transmitted, thereby optimizing the overall core timing parameters. This allows the memory to respond to execution actions at a faster speed and achieve ultra-high performance.
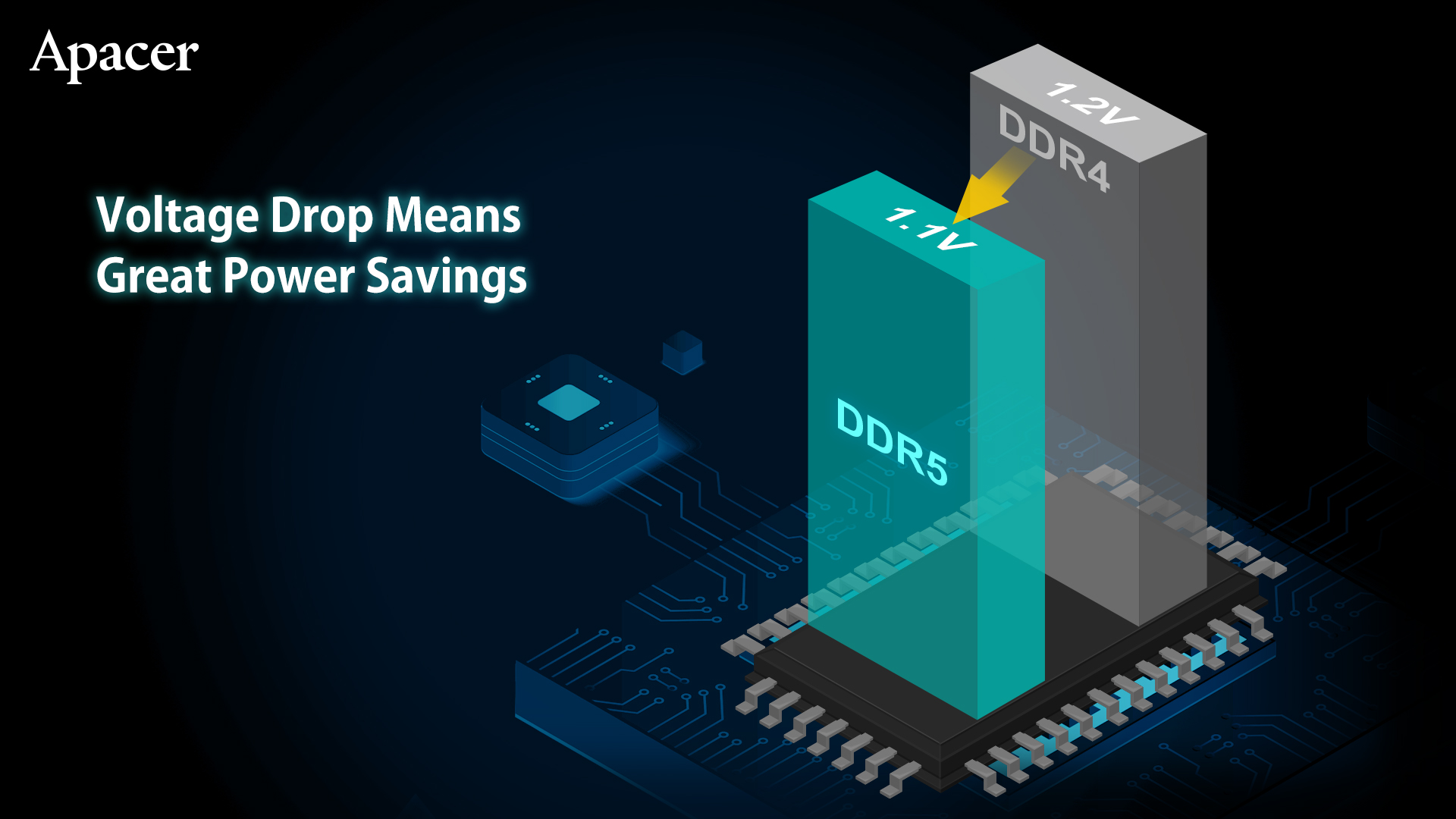
3. Voltage Drop Means Great Power Savings
The standard operating voltage of DDR5 memory is reduced from DDR4’s 1.2V to just 1.1V, which improves the power saving efficiency by 8%. This can reduce system power consumption and heat generation, especially for industrial systems that require low power consumption and have difficulties with heat dissipation. Server applications that require 24/7 operation also enjoy additional power saving benefits.
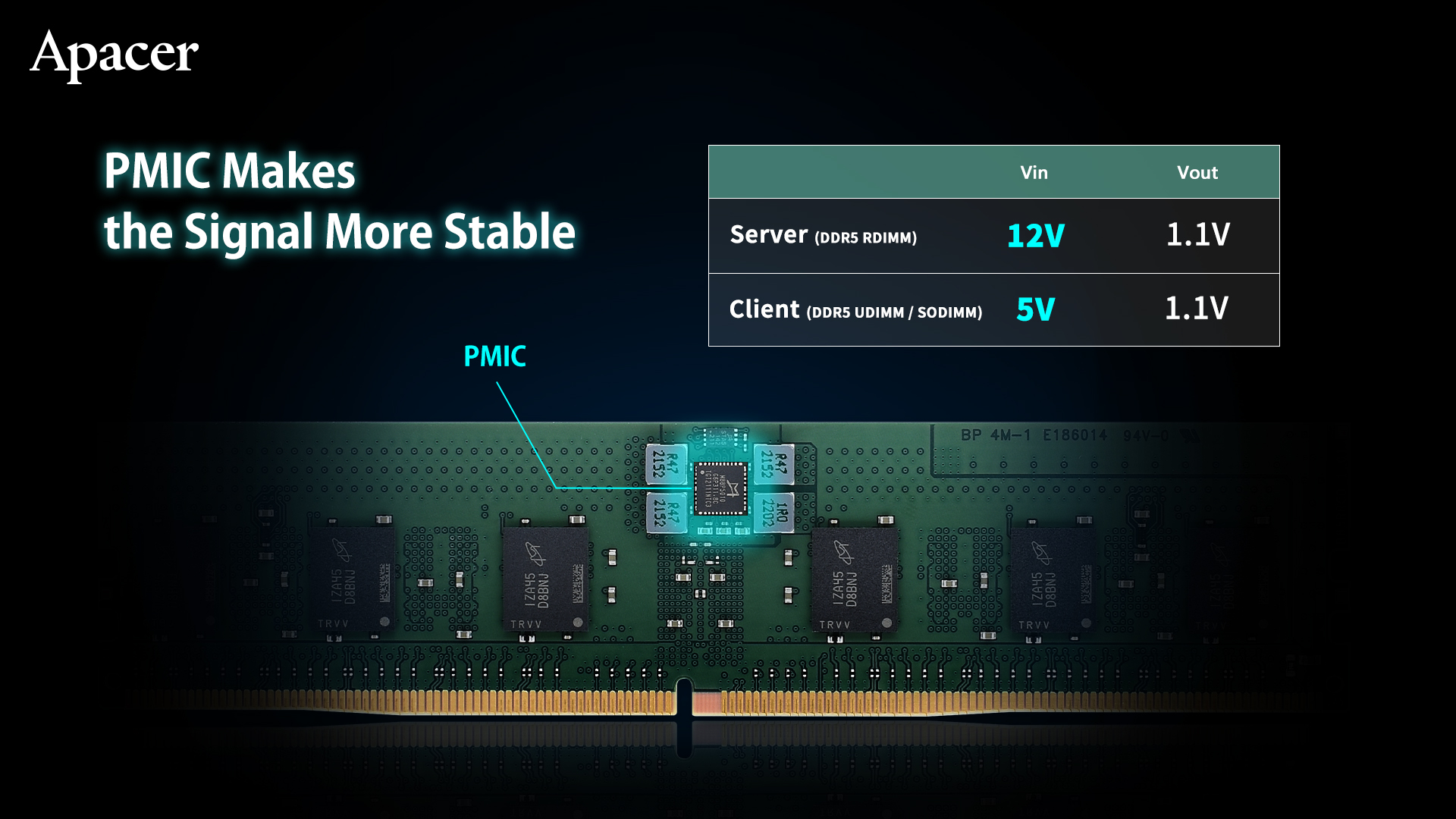
4. PMIC Makes the Signal More Stable
With the voltage reduced to 1.1V, in order to ensure voltage accuracy for stability during high-speed operations, DDR5 memory also adds power management functions. Instead of the traditional control method through the motherboard, the DDR5 memory is equipped with a power management IC (PMIC), which can control the system power load more efficiently and improve the power conversion efficiency by 85%. It thereby improves signal integrity and compatibility, and even reduces the cost of the motherboard design for power supply.
In addition, although they both output a working voltage of 1.1V, there are currently two PMIC specifications used in DDR5 memory. Unlike DDR5 UDIMM and SODIMM which use 5V PMICs; for server applications, DDR5 RDIMM server memory uses a 12V PMIC, and special attention should be paid to system platform design.
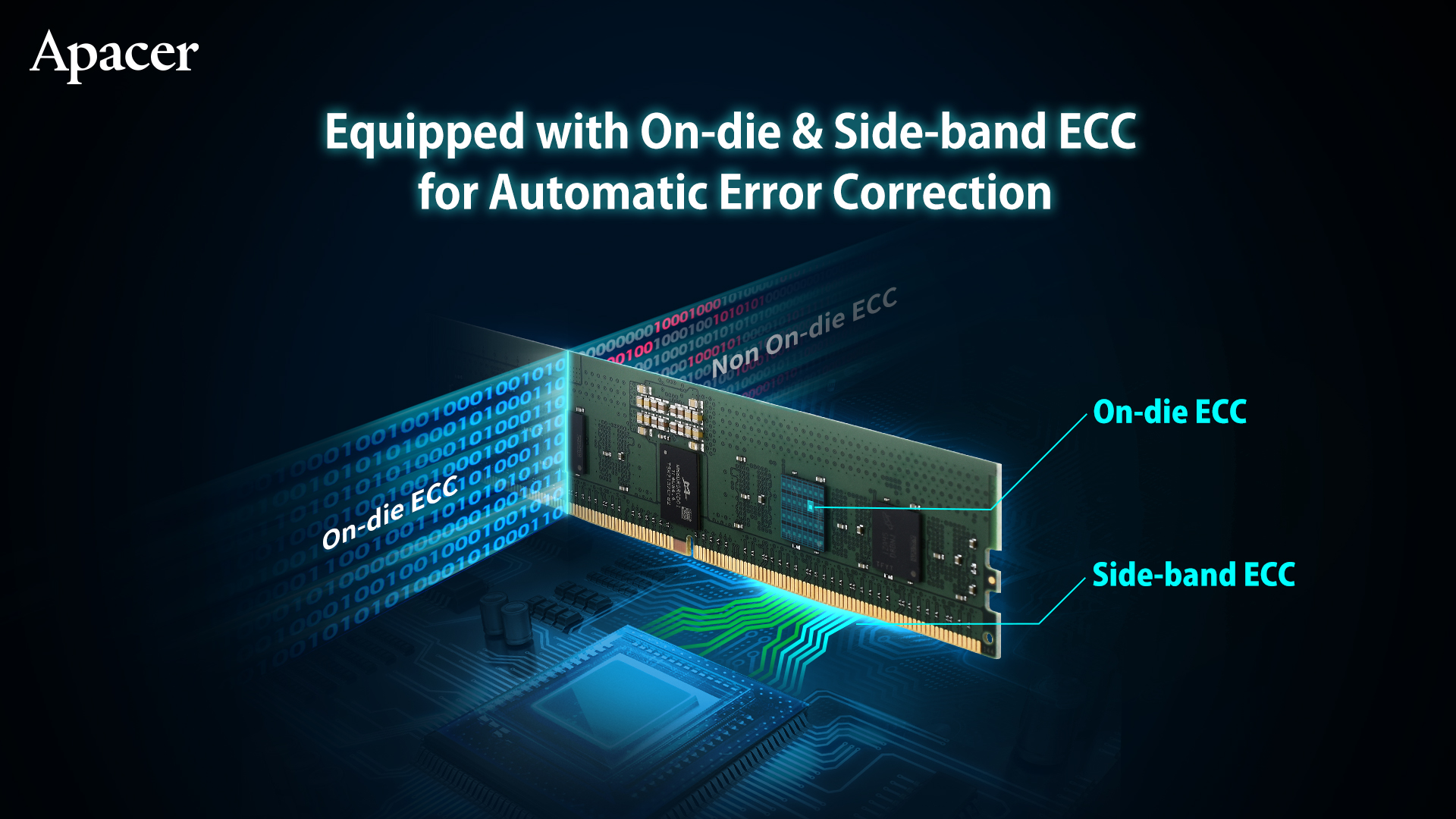
5. Equipped with On-die and Side-band ECC for Automatic Error Correction
In order to achieve higher performance, DDR5 memory has been improved in both capacity and data density. However, the technology scaling may also increase the risk of data errors. DDR5 RDIMM server memory supports On-die and Side-band ECC mechanisms, which can automatically detect and correct data errors in the memory. They provide end-to-end complete protection for the data transmission process and improve memory data fault tolerance, thereby improving data accuracy.
More importantly, this error correction mechanism also contributes to the stable and reliable performance of the system, meeting the reliability, availability and serviceability requirements of server applications for long-term operation.
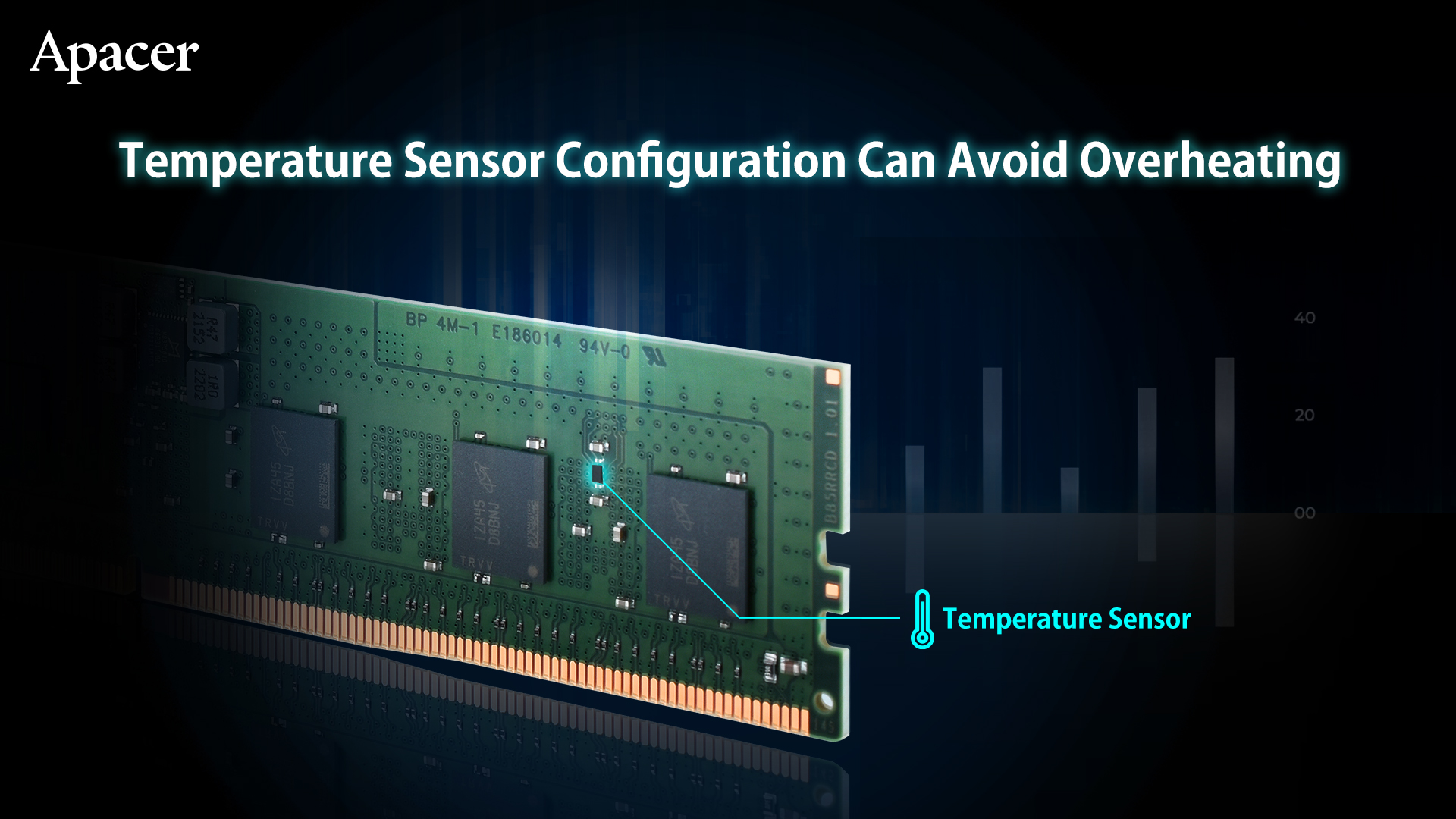
6. Temperature Sensor Configuration Can Avoid Overheating
In addition to adopting new components such as RCDs, PMICs and SPD hubs, DDR5 RDIMM server memory also adds a high-precision temperature sensor. This provides detailed memory temperature data to monitor the heat dissipation of the memory in real time. When designing the airflow of the system, the R&D personnel can also calculate the heat dissipation more accurately, avoiding excessive heat accumulation and affecting the stability of the system operation.
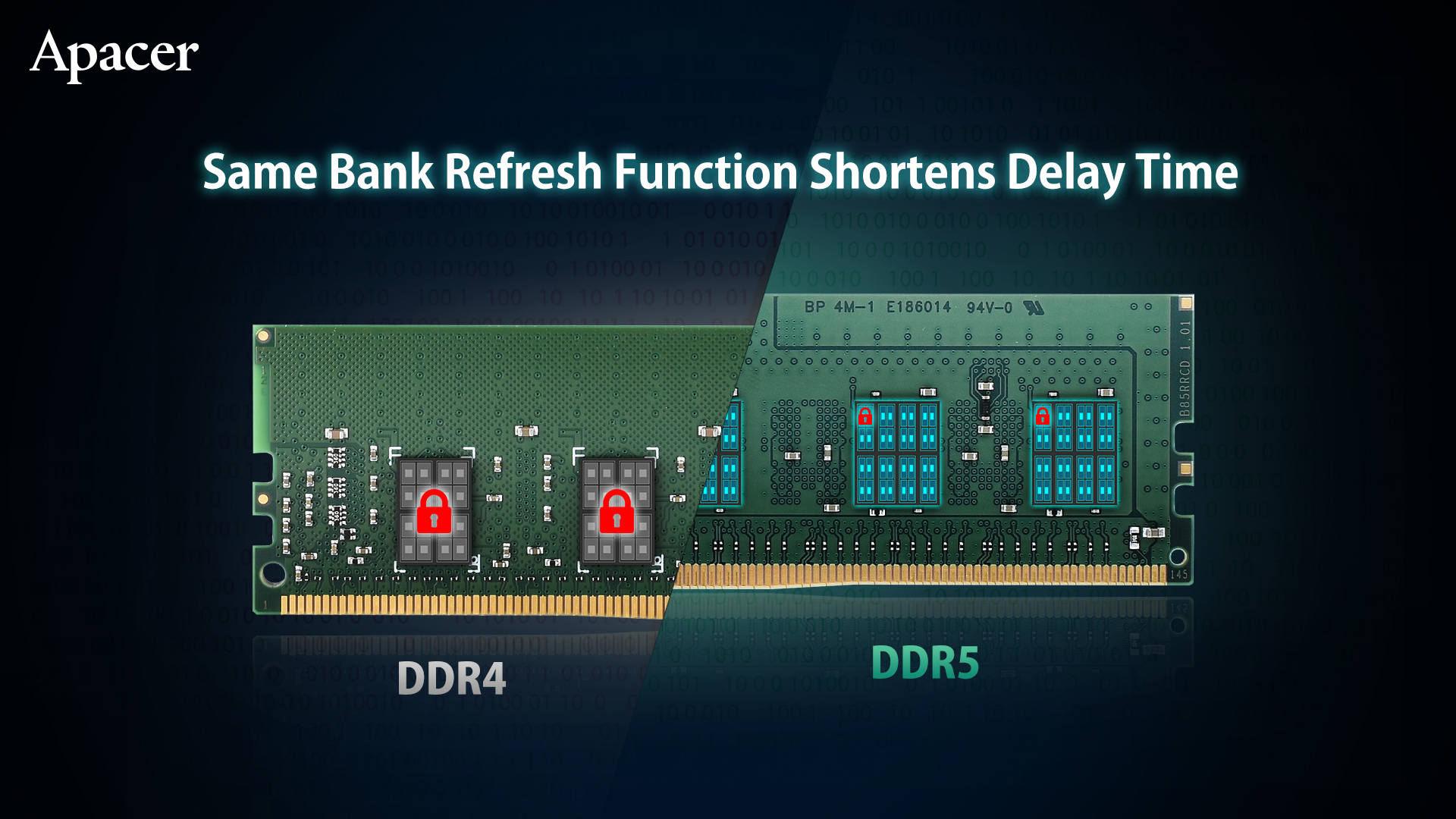
7. Same Bank Refresh Function Shortens Delay Time
In DDR4, for a refresh to occur, all banks need to be in an idle state and cannot execute other instructions at the same time. The Same Bank Refresh function of DDR5 memory allows the system to update a specific bank without affecting the access of other bank data, greatly reducing overall idle delay and improving system performance.
How Should You Choose DDR5 Memory Modules? Is It Time to Get On the DDR5 Technology Train?
The industrial market’s growing demand for scalable and energy-efficient infrastructure has made the transition to DDR5 unavoidable. As DDR5-enabled processor platforms continue to roll out, this is a critical moment for system developers and solution providers to adopt DDR5-based architectures. By supporting high-speed computing, advancing green computing objectives, and powering next-generation Embedded AI and edge computing systems, DDR5 memory is set to become a cornerstone technology for modern industrial applications. The following are some metrics that can be used as a reference for selecting DDR5 industrial memory products in the future.
1. Importance of the JEDEC 1.0 Mass Production Version Test
In the process of development and testing of DDR5 products, they must comply with the standards formulated by the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association and also be in accordance with the specifications of the mass production version recognized by JEDEC. At present, JEDEC has released the DDR5 RDIMM server memory 1.0 mass production standard. In other words, when selecting DDR5 RDIMMs, special attention should be paid to whether the manufacturer has completed the test in accordance with the JEDEC 1.0 standard specification, and is ready for mass production. At present, Apacer's DDR5 memory has completed the latest JEDEC mass production version test, and mass production is just around the corner.
2. Use of High-quality Original ICs
In key applications such as the industrial market, servers and data centers, the cost and goodwill lost due to downtime are often too large to measure. These applications cannot bear abnormal risks such as unstable memory quality. Industrial memory modules made with high-quality original DDR5 DRAM ICs from major manufacturers have extremely high product reliability and warranty protection, and are the first choice for industrial systems.
3. Support for Multiple Value-added Protection Technologies
The application scenarios of industrial memory are diverse, and server applications are no longer limited to running in indoor computer rooms with comprehensive environmental control equipment. How to improve the environmental resistance of DDR5 memory will be the key. At present, there are mature value-added protection technologies available on the market, such as Conformal Coating, Underfill, and Apacer's patented Anti-Sulfuration technology, all of which can protect the DDR5 module’s surface from external environmental challenges such as humidity, dust, environmental pollution, vibration and shock.